Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
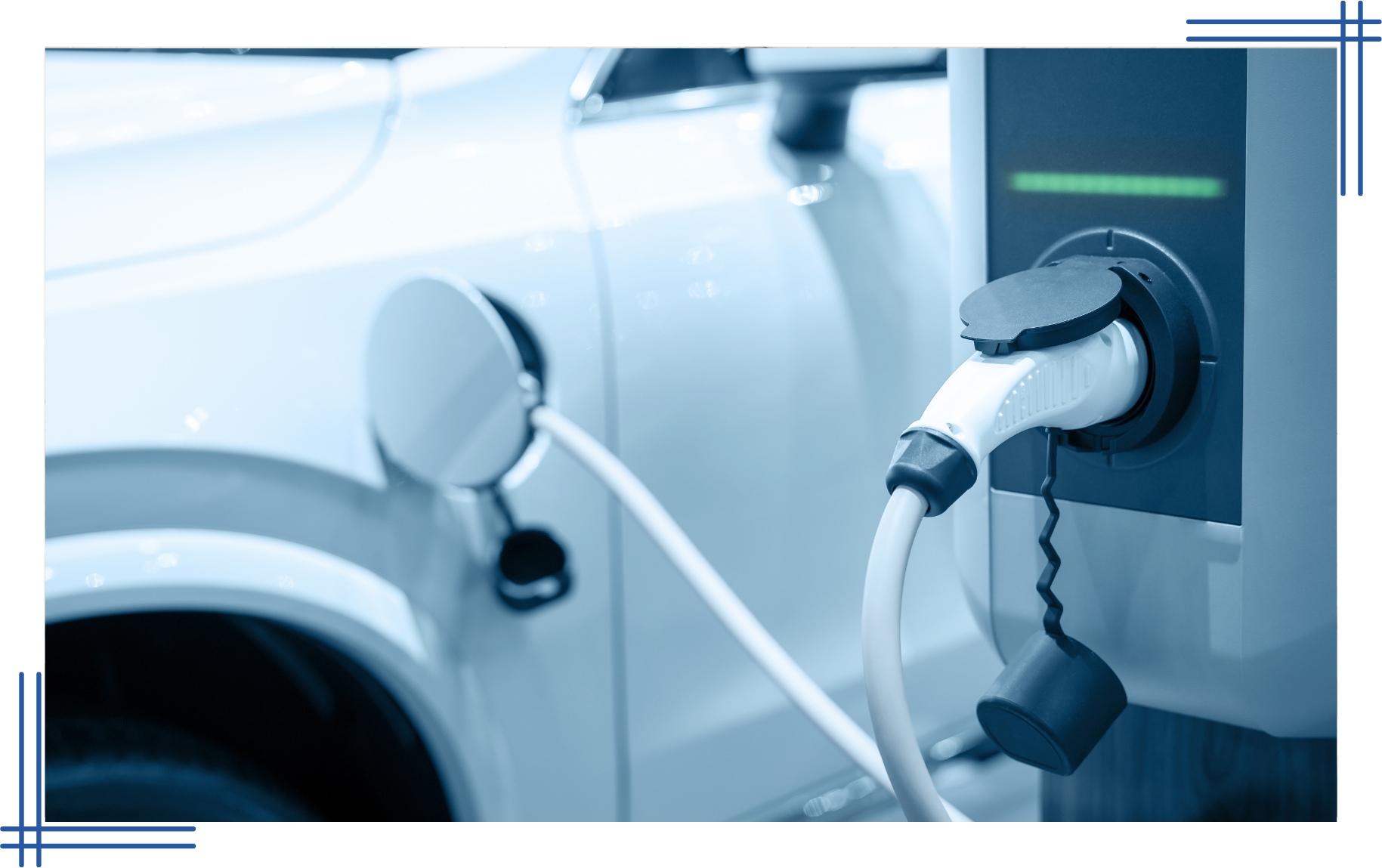
EV Charging Stations

Slide title
Write your caption hereButton
EV Charging Stations
Electric vehicles represent a significant shift in automotive technology and environmental policy. Traditionally powered by internal combustion engines burn fossil fuels. In contrast, electric vehicles, powered by electricity stored in rechargeable batteries, offer a cleaner alternative. This shift not only represents technological advancement but also aligns with global efforts to reduce carbon footprints.
The speed at which an EV can be charged is influenced by the ambient temperature. Charging can take longer in extremely cold weather. Batteries prefer a mild climate to operate efficiently, and some EVs even have thermal management systems to heat or cool the battery as needed during charging. Some support bi-directional charging, which means they can not only pull energy from the grid to charge their batteries but also push it back to the grid or use it to power a home during an outage. This feature essentially turns an EV into a mobile power bank.
Different Types
EV chargers are categorized based on their charging speed and power delivery capabilities, which significantly influence the convenience and usability of electric vehicles. There are three primary types of available, each serving different needs and scenarios. These include Level 1, Level 2, and DC Fast Chargers. Understanding the differences is essential for both consumers and stakeholders in the infrastructure sector.
Level 1: Level 1 provides the most basic level of charging and are typically included with the purchase of an electric vehicle. These require no special installation as they can be plugged directly into a standard household electrical outlet (110-120 volts). Level 1 is the slowest form of charging available, generally offering about 4 to 5 miles of range per hour. This type of is most suitable for overnight charging at home or for vehicles that are parked for extended periods. Due to its slower rate, Level 1 is often deemed sufficient for hybrid vehicles or for EV owners with minimal daily commuting distances. It represents the most accessible and cost-effective solution but is not practical for quick refueling during longer trips or for drivers with higher daily mileage needs.
Level 2: Level 2s are a significant step up from Level 1, operating on a 240-volt supply and typically found in residential, commercial, and public settings. These can provide about 12 to 80 miles of range per hour, making them considerably faster than Level 1. Level 2 is ideal for daily use and is commonly installed in private homes, public parking areas, workplaces, and commercial venues. The installation often requires some upgrades to support the higher voltage, which should include professional installation and potential upgrades to the building’s electrical panel. However, the convenience of faster charging makes Level 2 a popular choice for most EV owners who seek a practical solution that balances time and efficiency.
Level 3: DC Fast Chargers, also known as Level 3, represent the quickest technology currently available for electric vehicles. These chargers operate on a direct current (DC) rather than the alternating current (AC) used by Level 1 and Level 2, and they require significantly more powerful infrastructure. DC Fast Chargers can typically deliver 60 to 100 miles of range in just 20 minutes of charging, making them ideal for use along highways and in high-demand public stations. The high cost of DC Fast Charging stations and the substantial electrical grid upgrades necessary for their operation make them less common than Level 1 and Level 2. Nevertheless, they are necessary for facilitating long-distance EV travel and are often strategically placed at key locations to serve as a bridge between cities and across travel corridors.
Considerations For Home Charging
- Electrical Needs: The most common home chargers are Level 2, which require a 240-volt power source, similar to what large appliances like dryers use. Homeowners need to assess whether their current electrical system can handle the additional load or if an upgrade is necessary. This might involve increasing the capacity of the home’s electrical panel or installing a dedicated circuit for the EV charger.
- Placement: The location should be convenient and safe. Most homeowners choose to install chargers in their garages or driveways. Factors to consider include proximity to the electrical panel to minimize installation costs and the length of the charging cable to easily reach the vehicle.
- User Interface: Modern home chargers often come with advanced features such as programmable scheduling, Wi-Fi connectivity, and smartphone integration. These features allow users to monitor status, control charging times (to take advantage of lower electricity rates during off-peak hours), and track energy usage.
Benefits For Businesses
Businesses with charging stations can attract EV owners who prefer to shop or dine at locations where they can charge their vehicles. By providing charging stations at workplaces, it can enhance employee satisfaction and can be an incentive for employees considering an EV.
Businesses should plan for the future when installing EV charging stations. This means considering the potential for additional stations as the number of EV-driving customers and employees increases. To manage costs and energy load, businesses might need to implement energy management systems to optimize charging times and electricity use. Security measures are important to prevent unauthorized use or vandalism. This can include technological solutions like restricted access controls.
Don't let the future pass you by.
Contact Summit Electrical Solutions to find out how we can help you make the switch to electric with ease and confidence. Power your journey with us—your experts in electric vehicle solutions.
Frequently Asked Electric Vehicle Charging Questions
Q1: Can I use my EV to power my home during a blackout?
A1: Some modern EVs have "vehicle-to-home" (V2H) technology, allowing them to act as a backup generator. However, this requires specific equipment and compatible EV models.
Q2: Can an EV charging station increase the value of my home or property?
A2: Yes, installation can potentially increase the value of your property. As electric vehicles become more popular, home buyers are increasingly looking for properties that offer EV charging as a built-in amenity. This addition not only enhances convenience but also appeals to environmentally conscious buyers, potentially making your property more attractive and valuable in the real estate market.
Q3: Are there aesthetic customization options to match my home or business branding?
A3: Yes, customization options are available to align with home aesthetics or business branding. Manufacturers often offer various colors and finishes, and some even provide custom branding services that allow businesses to include logos, colors, and other design elements that reflect their corporate identity. This can enhance the visual appeal and brand consistency at commercial venues.
All Rights Reserved | Summit Electrical Solutions
